|
Business Organizations |
Financial Statements |
|
Sole Trader |
|
|
Partnership |
|
|
Limited Liability Company |
|
|
Co-operatives |
|
Financial Statements
- Profit and Loss Account/Income Statement – this is to ascertain profit or loss of a business over a given period.
- Balance Sheet – this is a financial listing of the assets, liabilities and capital of a business.
- Income and Expenditure Account – this is to record receipts and payments of a business.
- Appropriation Account – this section or account shows how the profit is to be apportioned.
- Cash Flow Statement – this is a financial statement that summarizes the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving a company.
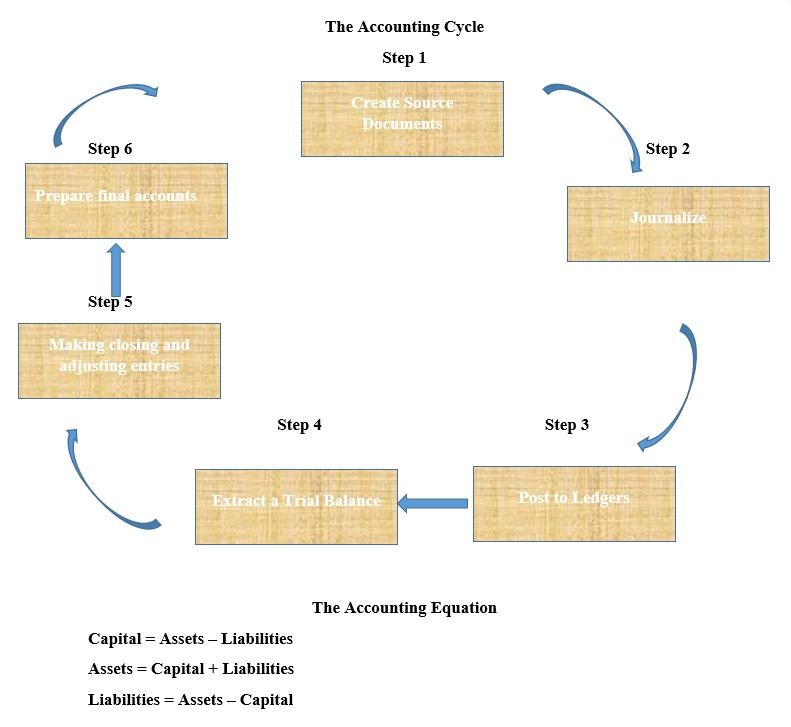
Accounting Cycle
The accounting cycle traces the various steps in which business transactions go through before they are finally analysed and presented as useful information reflecting the financial position of a company.
Assets are economic resources owned by a business that are used in its daily operations to generate profit and benefit the business. Simply, the assets are the resources own by the company. Assets can be classified as fixed assets and current assets.
Fixed Assets – are assets that are to be used by the business for a long period of time.
Examples:
- Building
- Motor vehicles
- Machinery
- Office equipment
- Furniture
- Fixtures
- Fittings
Current Assets – are assets that can be converted to cash easily or will be consumed within an accounting year. Such assets have a short life span.
Examples:
- Stock/Inventory
- Goods purchased for resale
- Debtors
- Accounting receivables – people who owe us
- Cash at bank
- Cash in hand
- Prepayments – monies the business pay in advanced
Liabilities are economic resources borrowed from an organization such as a bank. They are debts or monies that the business owes. Liabilities can be long term liabilities or current liabilities.
Long-term liabilities are monies owed by the business in which it has more than a year to repay it.
Examples:
- Mortgages and debentures.
- Long-term loans given by a bank.
Current liabilities are monies owed by the business that have to be repaid within the accounting year.
Examples:
- Creditors/accounts payables – organizations who the business owes.
- Bank overdraft – cash withdrawals from the current account exceeding the amount available.
- Accruals – unpaid money from goods and services.
Capital is investment made by the owner. It represents the owner’s interest in the business. It is the net worth of the business.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement or report which shows the financial position of the company at a particular date. The major components of a balanced sheet are:
- Assets – what the business owns.
- Liabilities – what the business owes.
- Capital or owner’s equity.
| Sample Balance Sheet | |
| Assets | $ |
| Motor Vehicle | 9,000 |
| Premises | 20,000 |
| Stock | 4,000 |
| Cash at Bank | 2,800 |
| Cash in Hand | 400 |
| Total Assets | 36,200 |
|
Liabilities |
|
| Creditor | 2,600 |
| Loan from the Bank | 12,000 |
| Total Liabilities | 14,600 |
| Capital (Assets – Liabilities) | 21,600 |
However, the balance sheet must balance where assets = liabilities + capital =
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
36,200 14,600 + 21,600
Types of Accounts
Some accountants divide all accounts as either personal accounts or impersonal accounts.
Personal accounts – divide accounts between debtors and creditors.
Impersonal accounts – divide accounts between real accounts and nominal accounts.
Real accounts are accounts in which property is recorded such as buildings, machinery, fixtures and stock.
Nominal accounts are accounts in which expenses, income, revenue and capital are recorded.